Invoice Guide
1. Overview
Welcome to this comprehensive invoicing guide.
It is designed to help you understand the importance of implementing a robust billing process, the essential aspects of a good invoice, and how to utilise the right invoicing tool to create and manage your account receivables effectively.
1.1 The definition of invoice
As defined by Investopedia: “An invoice is a time-stamped commercial document that itemizes and records a transaction between a buyer and a seller. If goods or services were purchased on credit, the invoice usually specifies the terms of the deal and provides information on the available methods of payment”. Invoice is also commonly known as “bill”, “sales invoice” and “VAT invoice”.
1.2 Why does a business need invoice?
Record keeping - it is a document that maintains the record of your business’s sales revenue.
Tax purpose – it contains necessary information to identify your tax liability on the supply of goods or services. Note: tax rate is subject to the tax law of your local jurisdiction.
Payment reminder – invoice also served as payment reminder, it clearly outlines the description, quantity and the price of the goods and services provided, and the agreed payment terms to remind the correspond client to settle the payment.
Business intelligence – when an effective invoicing process is established, business owners can make informed business decisions by analysing data generated from the daily invoicing activities such as aged debtors report, project profitability, cash flow statement, revenue forecast, etc.
Branding and marketing – a well-designed professional invoice and friction-free billing process give a good impression to client and increase brand awareness.
2. Invoice requirements
The requirements may differ slightly depending on your business operation jurisdiction. We have outlined the most widely adopted requirements as below:
A unique identification number (invoice number)
Your business name, address and contact information
The business name and address of the client you are invoicing
A clear description of the goods and services you are charging for
Details of quantities of goods, if applicable
The issue date of the invoice
Tax amount if applicable. i.e. VAT, sales tax
The gross, total amount of the invoice
Others
VAT number if applicable
Company registration number if applicable
Director information if applicable
Payment instructions
Terms of the invoice
3. Invoice best practice
Invoice best practice refers to a set of guidelines on company’s billing procedures that is generally accepted within/in the industry and known to produce the desired outcome.
Businesses often fail to establish a robust billing process along with its growing operating activities due to lack of adoption of invoice best practices. For example, excessive manual process is prone to human input errors, failing to enforce a collection policy will lead to potential late payment and inadequate discount granted to customers may discourage early settlement; which all in turn will negatively impact your working capital/cash flow.
Business should consider the following best practices to ensure accuracy and timely invoicing.
Automation - use an automated electronic billing system such as antbill online invoicing system to save time and reduce human error.
save and reuse company, client and product details to reduce manual data input
invoices can be generated and sent to client automatically
able to generate emails to clients, such as invoice notification email and payment reminder email
system generated billing reports facilities business decision
Timely/effective invoice generation and reporting – invoices should be raised in a timely manner where possible.
Enforce collection policies – take proactive approach on payment collection where you should
Agree payment terms with client in advance and stick to them
Periodic review on account receivables and take actions on potential late payments
Set clear procedures on dealing with overdue invoices
Communicate efficiently – establish a communication channel with client and set expectations, communicate your billing policies with your client in advance, make sure to follow up on payment before invoices become overdue.
Use KPIs – key performance indicators are great to evaluate how effective is your billing process. You will get a clear picture on the percentage of clients who pay late bad debt write-off, and the average number of days between receiving the payment and the issuance of the invoices. Commonly adopted account receivable KPIs includes:
Days Sales Outstanding (DSO)
Turnover Ratio
Collections effectiveness index (CEI)
Bad Debt to Sales Ratio
Number of revised invoices
4. Billing Process
A typical billing process involves two-way interaction between the service provider and the client, which can be summarized into four steps as below:
Step 1: The service provider aggregates billing information and generates invoice data based on the client’s activity in the preceding month. See Figure 4.1 Invoicing Process Flow Chart
Step 2: The service provider sends one invoice to each client by default unless requested otherwise
Step 3: The client records the invoice data in their system and performs relevant internal processes e.g. reconciliation of the invoice received.
Step 4: The invoiced payment amount is remitted to the service provider before due date stated on the invoice. The payment method is agreed in advance between the provider and the client
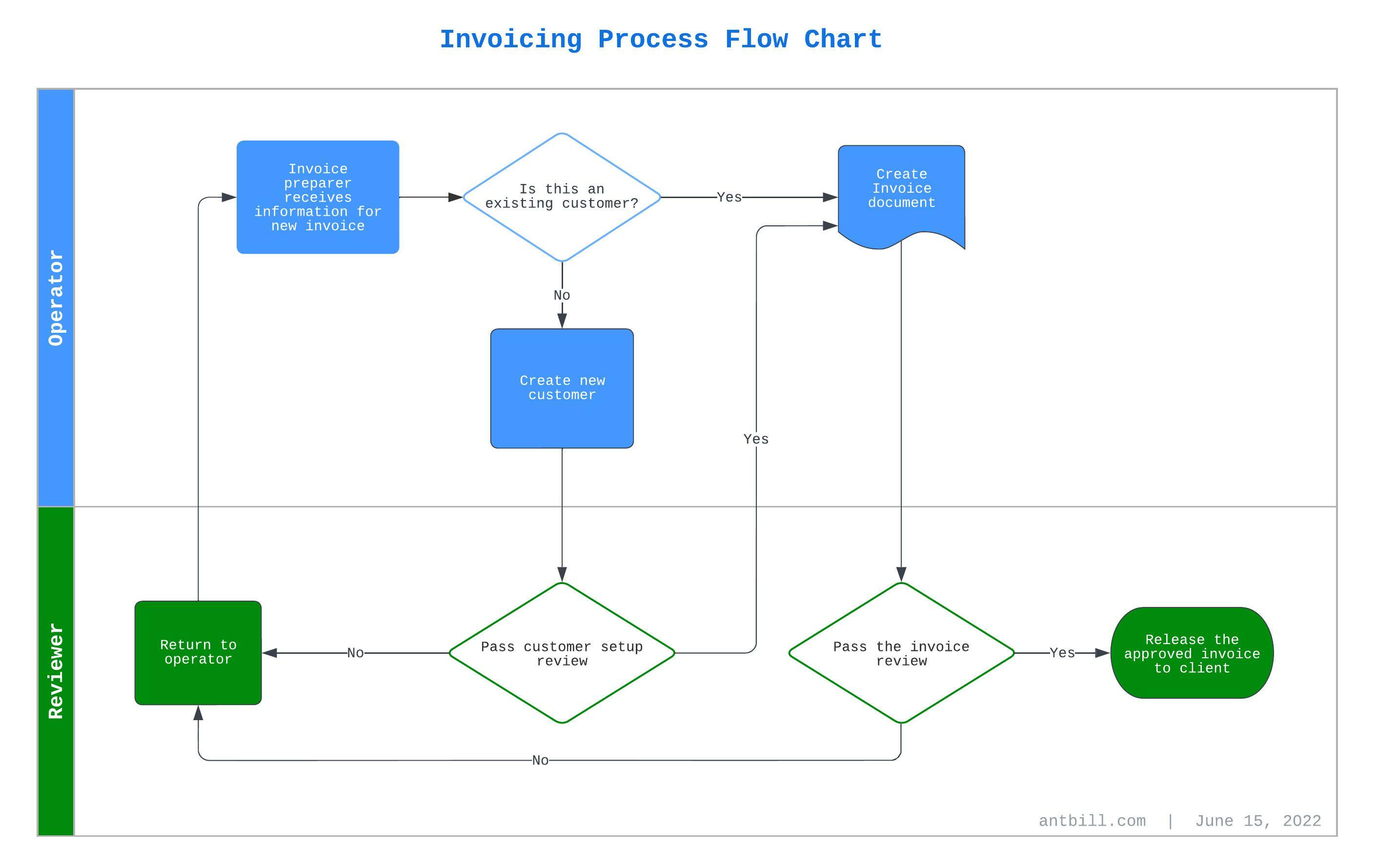
Figure 4.1 Invoicing Process Flow Chart
5. Choose the right invoicing tool
As a busy business owner, weather using an offline manual process or a comprehensive online billing system. The ability to be able to manage the account receivable process efficiently and accurately is an essential part of your business success.
Although we recommend all business owners to adopt the billing best practises. However, in reality, depending on the size, budget and nature of the business operating activities such as billing frequency and staffing, business owners tend to create and manage their invoices differently.
We have compared the most widely adopted invoice creation methods/tools as below. By clearly listed out the advantages and disadvantages of each, we are hoping this can help you to pick the right option that best suits your business need.
5.1 Word/Excel Invoice Template
Pros
| Overall Invoice templates is a viable solution for new businesses when complex invoicing process isn’t required as billings aren’t frequent. However, a manual billing process in long run is not recommended as to manage invoices and account receivables manually is a tedious and error prone task even for experienced professionals. |
Cons
|
5.2 PDF Invoice Generator
Pros
| Overall The pdf invoice generator is a great way allow new businesses to create and send professional looking invoice and when it is a once off and low volume task. However, the lack of ability to store invoices online, track and manage existing invoices prevent it to be a long term billing solution for growing businesses. |
Cons
|
5.3 Antbill Online Invoicing
Pros
| Overall No matter you are just starting your business journey or you have already been a large enterprise, a robust billing process is the corner stone for any businesses to be success. With all the benefits and functionalities it provides, we recommend use antbill online invoicing or any other professional online invoicing software as your long term billing management solution. |
Cons
|
6. Glossary
Accounts receivable (AR) tracks the money owed to a person or business by its debtors. It is the functional opposite of accounts payable.
Aging Report is a type of report that consists of the collections of unpaid client invoices or credit memos that are arranged by date ranges. I.e. 30 days, 60 days.
Average Collection PeriodAverage Collection Period is the average number of days between the dates that the money was received from the clients and issuance of the invoices.
Bad DebtBad Debt is an expense that a business incurs once the repayment of credit previously extended to a client is deemed to be uncollectible.
Collection Effectiveness Index (CEI): The matrix used to calculate the company’s ability to retrieve their accounts receivable from its clients.
Credit & Collections Policy: written guidelines that set the terms and conditions for supplying goods on credit, client qualification criteria, procedure for making collections, and steps to be taken in case of client delinquency.
Customer Credit: The credit given by the company to its clients, which they have to pay within the credit limit.
Cash flow (CF) describes the balance of cash that moves into and out of a company during a specified accounting period.
Days Sales Outstanding (DSO) is a metric used to calculate the average time a company takes to collect revenue after the sale has been made. Formula: DSO = (Account Receivable / Total Credit Sales) * Number of Days
Delinquency Predictor Score estimates the chance your business will ask for legal relief from creditors, shut down without satisfying its debts in the next 12 months, or show other signs of “severe delinquency.”
Duplicate Payment: A client paid more than once for the service they’ve received. Such transactions are made when the accounts payable systems that failed to recognize previous payments.
Early Payment Discount Reminder: The message sent to a client for paying before a certain time to be awarded a discount.
General Ledger: The accounting record that contains double-entry bookkeeping which allows a business to keep track of all incoming and outgoing cash flow.
Past due Receivables refers to payments that have not been made by its agreed cut-off time at the end of its due date.
Payment Terms outline how, when, and by what method your clients or clients provide payment to your business.
Periodic Review: Updating of business master data such as client credit limit and client contact details in specific time intervals for better accuracy.
Remittance can be defined as the document sent by the client to the seller, informing the seller of an invoice which is paid.
Sales Invoice: an accounting document that records goods sold or services provided to a client and how much money the client owns to the seller.
Sales Tax is a tax paid to a governing body for the sales of certain goods and services.
Value-Added Tax (VAT) is a tax, which is payable on sales of goods or services within the territory of the Member States of the EU.
Write-OffsWrite-Offs in account receivable setting is the debt that cannot be recovered or collected from a debtor is bad debt.